이 글은 Routing and Query Construction 보고 정리한 글입니다.
Routing and Query Construction
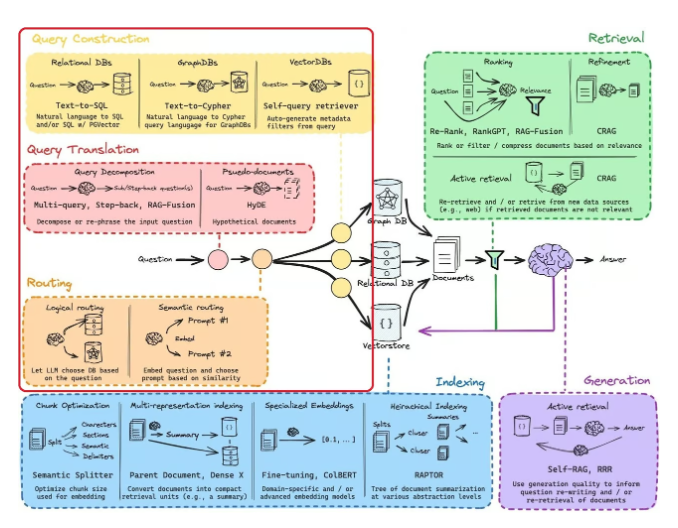
Routing Component:
- RAG 시스템의 요소 내에서 사용자의 질문을 이해한 후, 질문을 어디로 보낼지 결정하는 컴포넌트임.
- RAG 시스템에서는 벡터 스토어 뿐 아니라 여러 데이터베이스들도 있을거기 때문에 라우팅을 통해 적절한 데이터 소스를 선택하는 기능이 필요함.
두 가지 Routing 기법:
- Logical Routing
- Semantic Routing
Logical Routing 기법:
- 사전에 정의된 데이터 소스가 있다고 했을 때, Query 와 Context 를 보고 어떤 데이터 소스로 보낼지 결정하는 기법임.
LangChain 에서 Logical Routing 을 이용하는 예시는 다음과 같다:
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from typing import Literal
class QueryRouter(BaseModel):
"""Route a user query to the appropriate datasource that will help answer the query accurately"""
datasource: Literal['lora', 'bert', 'general'] = Field(...,
description="Given a user question choose which datasource would be most relevant for answering their question"
)
question: str = Field(..., description="User question to be routed to the appropriate datasource")
llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4',temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(QueryRouter)
router_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are an expert router that can direct user queries to the appropriate datasource. Route the following user question about a topic in NLP and LLMs to the appropriate datasource.\nIf it is a general question not related to the provided datasources, route it to the general datasource.\n"),
("user", "{question}")
]
)
router = (
{'question': RunnablePassthrough()}
| router_prompt
| structured_llm
)
question = "How does the BERT work?"
result = router.invoke(question)
qa_prompt = hub.pull('rlm/rag-prompt')
def choose_route(result):
llm_route = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4',temperature=0)
if "bert" in result.datasource.lower():
print(f"> Asking about BERT ...\nQuestion: {result.question}\nAnswer:")
bert_chain = (
{'context': retriever_bert, 'question': RunnablePassthrough()}
| qa_prompt
| llm_route
| StrOutputParser()
)
return bert_chain.invoke(result.question)
elif "lora" in result.datasource.lower():
print(f"> Asking about LoRA ...\nQuestion: {result.question}\nAnswer:")
lora_chain = (
{'context': retriever_lora, 'question': RunnablePassthrough()}
| qa_prompt
| llm_route
| StrOutputParser()
)
return lora_chain.invoke(result.question)
else:
print(f"> Asking about a general question ...\nQuestion: {result.question}\nAnswer:")
general_chain = llm_route | StrOutputParser()
return general_chain.invoke(result.question)
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableLambda
full_chain = router | RunnableLambda(choose_route)
full_chain.invoke("What are the benefits of LoRA?")
Semantic Routing 기법:
- Query 를 보고 쿼리에 임베딩 유사도 검색을 통해서 유사한 Prompt 를 찾아서 사용하는 기법임.
- 그러니까 쿼리를 바탕으로 router prompts 를 찾는거임.
LangChain 에서 Semantic Routing 을 사용하는 코드는 다음과 같다:
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{question}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down hard problems into their component parts, \
answer the component parts, and then put them together to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{question}"""
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings()
routes = [physics_template, math_template]
route_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents(routes)
len(route_embeddings)
from langchain.utils.math import cosine_similarity
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
def router(input):
# Generate embeddings for the user query
query_embedding = embeddings.embed_query(input['question'])
# Getting similarity scores between the user query and the routes. This contains the similarity scores between the user query and each of the two routes.
similarity = cosine_similarity([query_embedding], route_embeddings)[0]
# Find the route that gives the maximum similarity score
route_id = similarity.argmax()
if route_id == 0:
print(f"> Asking a physics question ...\nQuestion: {input['question']}\nAnswer:")
else:
print(f"> Asking a math question ...\nQuestion: {input['question']}\nAnswer:")
return PromptTemplate.from_template(routes[route_id])
semantic_router_chain = (
{'question': RunnablePassthrough()}
| RunnableLambda(router)
| ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4',temperature=0)
| StrOutputParser()
)
semantic_router_chain.invoke("What is the formula for the area of a circle?")
Query Construction 소개:
- 이제 Routing 을 했으니, 데이터 스토어에서 검색할 수 있도록 해야함. 그러니까 데이터베이스 조회 언어로 변경하는 작업을 해야하는거지. 대표적인 걸로 Text-to-SQL 이 있음.
Query Construction 기법:
- 전체 스키마 정보를 넘겨주는 방법 (= Entire Schemae)
- Scheme RAG 를 이용하는 방법. (RAG 를 통해서 필요한 Scheme 를 검색하는 기법임)
- 텍스트를 SQL 로 변경해주는 작업을 Fine-tuning 을 통해 학습한 언어 모델을 사용하는 것.
- 철자가 틀린 사용자 질문의 경우 Vector Store 에서 검색해서 올바른 철자를 찾는 방식을 적용할 수도 있네.
Query Construction 에 대해서는 아직까지는 SQL 문을 잘 생성해주는 능력이 부족한듯하다.
- Scheme RAG + Fine-tuning + ICL (InContext Learning) 을 GPT 4에 해도 80% 초반임.
- 이걸 할거라면 모델의 성능이 중요하곘고, 이 작업이 실패할 것에 대한 고려가 중요함.
다음은 LangChain 에서 Query Construction 을 사용하는 예제임. 주어진 질문을 보고 Youtube 동영상 검색을 위해 메타데이터 필터를 만드는 예제:
from langchain_community.document_loaders import YoutubeLoader
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnablePassthrough
docs = YoutubeLoader.from_youtube_url(
"https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sVcwVQRHIc8", add_video_info=True
).load()
docs[0].metadata
import datetime
from typing import Optional
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
class TutorialSearch(BaseModel):
"""Search over a database/playlist of videos about LLMs and Langchain."""
content_search: str = Field(
...,
description="Similarity search query applied to video transcripts.",
)
title_search: str = Field(
...,
description=(
"Alternate version of the content search query to apply to video titles. "
"Should be succinct and only include key words that could be in a video "
"title."
),
)
min_view_count: Optional[int] = Field(
None,
description="Minimum view count filter, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
max_view_count: Optional[int] = Field(
None,
description="Maximum view count filter, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
earliest_publish_date: Optional[datetime.date] = Field(
None,
description="Earliest publish date filter, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
latest_publish_date: Optional[datetime.date] = Field(
None,
description="Latest publish date filter, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
min_length_sec: Optional[int] = Field(
None,
description="Minimum video length in seconds, inclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
max_length_sec: Optional[int] = Field(
None,
description="Maximum video length in seconds, exclusive. Only use if explicitly specified.",
)
def pretty_print(self) -> None:
for field in self.__fields__:
if getattr(self, field) is not None and getattr(self, field) != getattr(
self.__fields__[field], "default", None
):
print(f"{field}: {getattr(self, field)}")
meta_data_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are an expert at converting user questions into database queries. \
You have access to a database of tutorial videos about LLMs and Langchain. \
Given a question, return a database query optimized to retrieve the most relevant results."
),
("user", "{question}")
]
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model='gpt-4',temperature=0)
structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(TutorialSearch)
meta_data_chain = (
{'question': RunnablePassthrough()}
| meta_data_prompt
| structured_llm
)
query = meta_data_chain.invoke("Build RAG using Langchain videos published before January 2024 with at least 1000 views.")
query.pretty_print()
'Generative AI > RAG' 카테고리의 다른 글
| BM42: New Baseline for Hybrid Search (0) | 2024.07.06 |
|---|---|
| Advanced RAG Series: Generation and Evaluation (0) | 2024.06.19 |
| Advanced RAG Series: Retrieval (0) | 2024.06.18 |
| Advanced RAG Series: Query Translation (0) | 2024.06.12 |
| Advanced RAG series: Indexing (0) | 2024.06.05 |